Details of the Initiative
Eating too much salt is likely to lead to the development and severity of lifestyle-related diseases such as high blood pressure and chronic kidney disease, and is a social issue related to health. Although a salt intake of less than 6.0 g/day is considered desirable to prevent severe lifestyle-related diseases, the actual daily salt intake in Japan is 10.9 g for adult men and 9.3 g for adult women. So, can you reduce salt in your usual diet? Can you put up with low-salt food that many people feel bland?
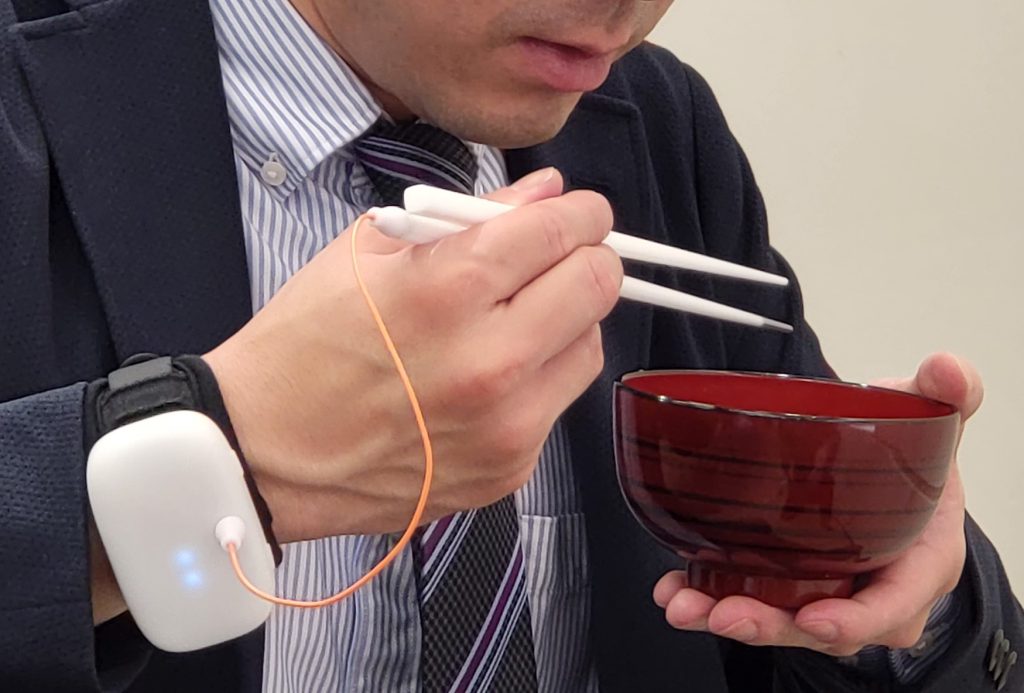
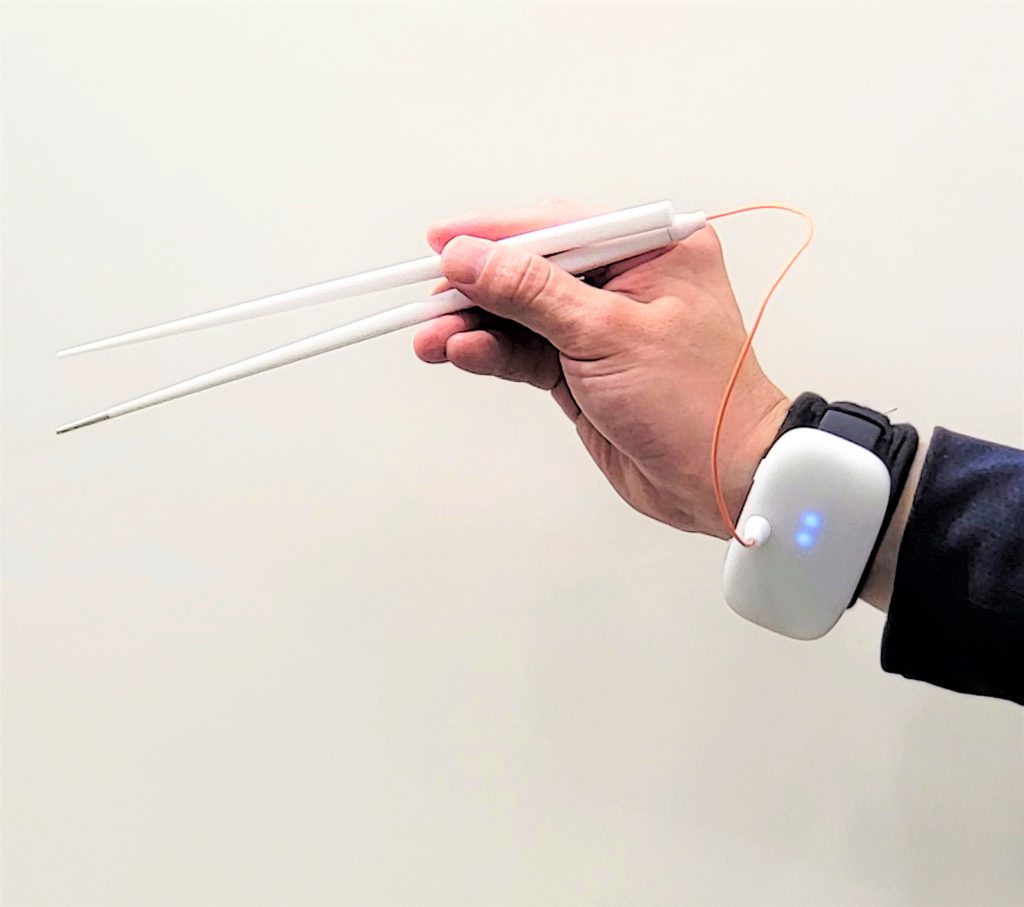
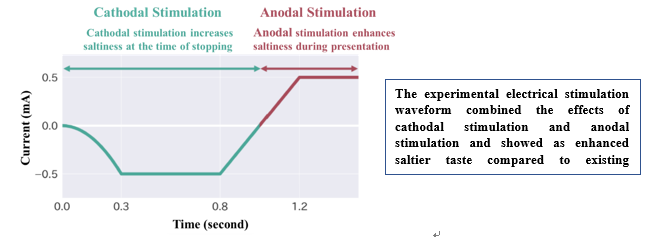
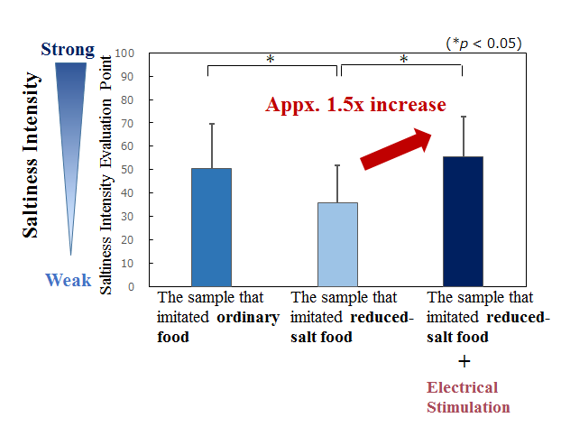
Miyashita’s laboratory has been conducting research for more than 10 years on electric taste tableware that changes the way people perceive taste. Using very weak electricity that does not affect the human body, the functions of ions such as sodium chloride, which is the base of saltiness, and monosodium glutamate, which is the base of umami, are adjusted so that the taste of food can be made to feel strong in a simulated way. In the clinical trial conducted on people who eat a low-salt diet on a daily basis, it was confirmed that the saltiness felt when eating a low-salt diet was enhanced by approximately 1.5 times.
Kirin Holdings has promoted the social implementation of this device. Technology makes it possible to enjoy a rich taste and to maintain physical health.